Regenerative agriculture is a holistic land management practice that focuses on regenerating and revitalizing the health of the soil, enhancing biodiversity, and improving the water cycle. It's a paradigm shift from conventional agriculture, aiming to work with, rather than against, nature. By nurturing the soil and surrounding ecosystems, regenerative agriculture has the potential to mitigate climate change, increase food security, and create sustainable farming systems. Let's delve into the principles and benefits of regenerative agriculture that are reshaping the future of farming and the planet.
1. Building Healthy Soil: At the heart of regenerative agriculture is the emphasis on soil health. Healthy soil is teeming with life, rich in organic matter, and has a balanced microbial ecosystem. Practices such as minimal tillage, cover cropping, and organic amendments help to enhance soil structure and fertility. Healthy soil not only provides an optimal foundation for crop growth but also sequesters carbon, mitigating the impacts of climate change.
2. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Restoration: Regenerative agriculture aims to foster diverse and resilient ecosystems on and around farms. By incorporating diverse crop rotations, integrating agroforestry practices, and creating habitat corridors, farmers can support a wide array of plants, insects, and wildlife. This approach not only enhances natural pest control and pollination but also contributes to the preservation of native flora and fauna.
3. Water Conservation and Quality: Effective water management is a central tenet of regenerative agriculture. By improving soil structure and organic matter content, the land becomes more adept at retaining water, reducing erosion, and minimizing runoff. Practices such as keyline design and rainwater harvesting are employed to optimize water usage, while also preventing contamination of water bodies with agricultural runoff.
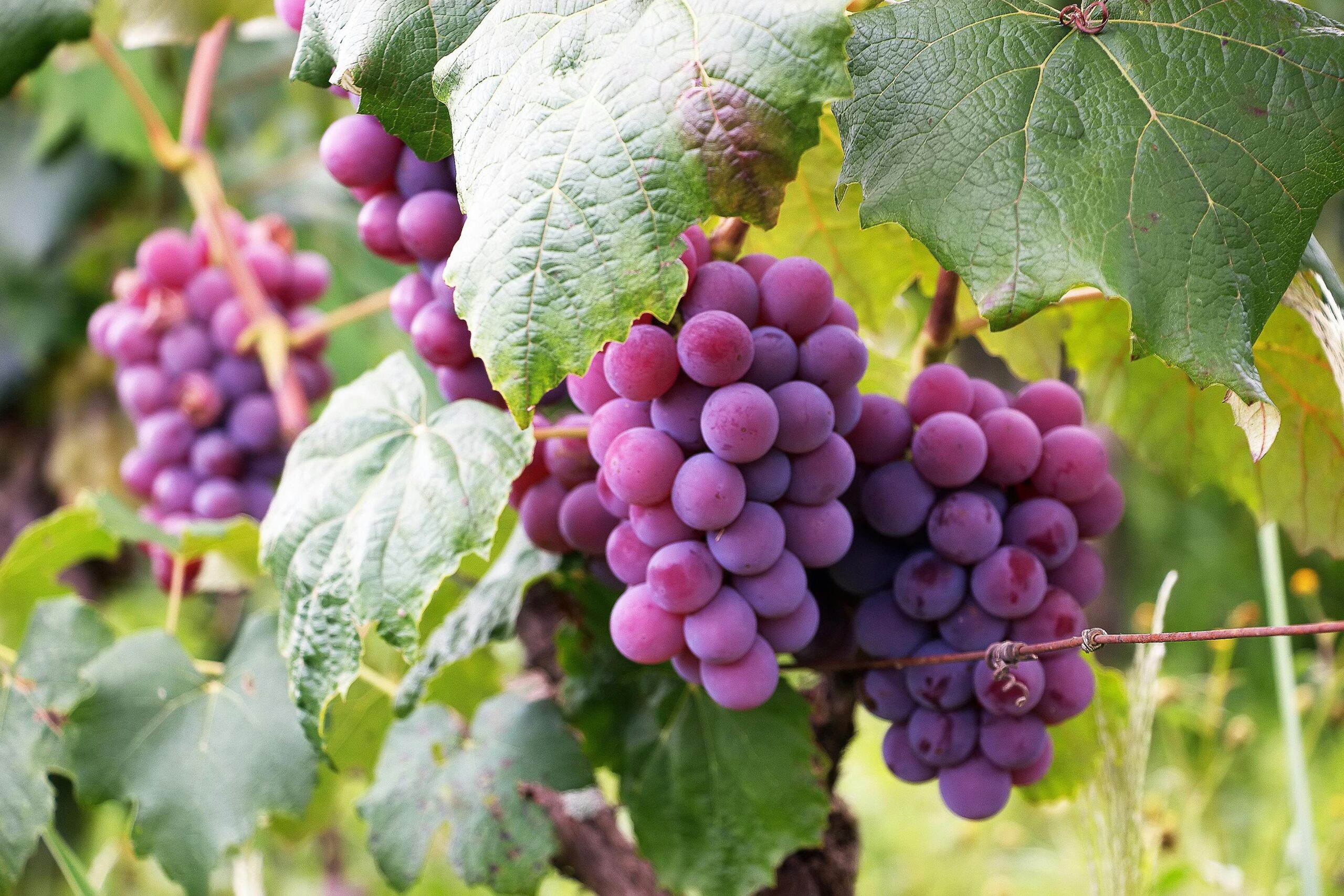

4. Carbon Sequestration: As a response to the climate crisis, regenerative agriculture plays a critical role in sequestering carbon from the atmosphere and storing it in the soil. Through the build-up of soil organic matter and the use of perennial vegetation, regenerative farming practices act as a carbon sink, helping to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
5. Economic and Community Benefits: By promoting regenerative practices, farmers can potentially reduce input costs, improve yields, and create more resilient agricultural systems. This approach also fosters stronger connections between farmers and their local communities, supporting regional food systems and economies.
The Future of Farming: Regenerative agriculture represents a fundamental shift towards more sustainable and regenerative farming practices, offering a promising alternative to industrial agriculture. By nourishing the land, prioritizing ecological balance, and mitigating climate change, this approach holds the potential to transform the food and agriculture industry. It has the capacity to not only provide nutritious food but also to restore the vitality of the earth for future generations.
As consumers, we can support regenerative agriculture by seeking out foods produced using these principles, advocating for agricultural policies that incentivize regenerative practices, and engaging with local farmers who embrace these methods. Together, we can be part of a global movement towards a more regenerative and sustainable future.
Michaela Pontiki